Can Rlog Be Applied For Data With No Replicates
Nigh GEO2R
Background
GEO2R is an interactive web tool that allows users to compare 2 or more groups of Samples in a GEO Series in order to identify genes that are differentially expressed across experimental conditions. Results are presented as a tabular array of genes ordered by significance, and every bit a collection of graphic plots to assistance visualize differentially expressed genes and assess data set quality.
GEO2R performs comparisons on original submitter-supplied processed data tables using the GEOquery and limma R packages from the Bioconductor project. Bioconductor is an open source software projection based on the R programming language that provides tools for the assay of loftier-throughput genomic data. The GEOquery R packet parses GEO data into R data structures that can be used by other R packages. The limma (Linear Models for Microarray Assay) R package has emerged as one of the most widely used statistical tests for identifying differentially expressed genes. It handles a wide range of experimental designs and data types and applies multiple-testing corrections on P-values to help correct for the occurrence of false positives. Thus, GEO2R provides a simple interface that allows users to perform R statistical analysis without command line expertise.
Dissimilar GEO's other DataSet analysis tools, GEO2R does not rely on curated DataSets and interrogates the original Series Matrix data file directly. This allows a greater proportion of GEO data to be analyzed in a timely mode. Nevertheless, information technology is of import to realize that this tool can access and analyze almost any GEO Series, regardless of data type and quality, so the user must exist aware of GEO2R Limitations and caveats.
How to use Back to acme
Enter a Series accession number
If you followed a link from a Series tape, the GEO accession box will already be populated. Otherwise, enter a Series accession number in the box, e.g., GSE25724. If the Serial is associated with multiple Platforms, you will be asked to select the Platform of interest.
Define Sample groups
In the Samples panel, click 'Define groups' and enter names for the groups of Samples y'all program to compare, e.g., test and control. Upwards to 10 groups can exist divers. At to the lowest degree ii groups must exist defined in social club to perform the assay. Groups can be removed using the [X] feature next to the group name. [New] The order in which you ascertain the groups has a bearing on downstream results. For two group comparisons, typically it is appropriate to define the exam group first, then define the control group - that way, the log fold change direction will follow convention and be positive for genes upregulated in examination samples compared to controls, and negative for downregulated genes. (Note: This change was implemented November 2020. You can reverse the order in which groups are created if you need to replicate a previous analysis).
Assign Samples to each grouping
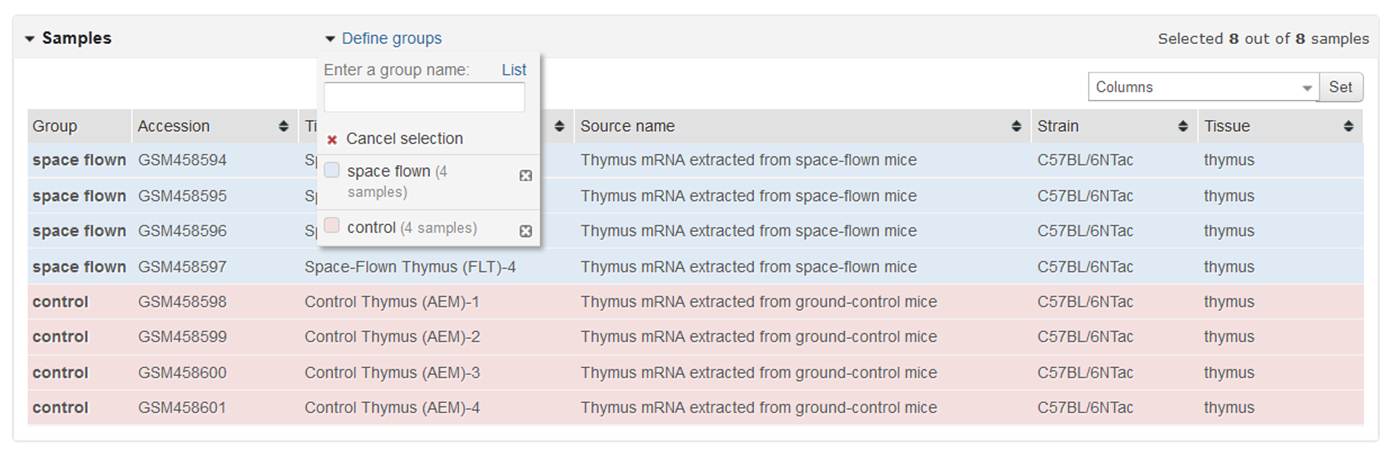
To assign Samples to a group, highlight relevant Sample rows. Multiple rows may be highlighted either by dragging the cursor over face-to-face Samples, or using Ctrl or Shift keys. When relevant Samples are highlighted, click the grouping proper noun to assign those Samples to the grouping. Repeat for each group. Non all Samples in a Series need to be selected for the analysis to work.
Use the Sample metadata columns to aid determine which Samples vest to which group. The tabular array is populated with Accession, Championship, Source name and private Characteristics fields from the Sample records. Y'all tin can change which fields are displayed using the Columns box at the upper correct corner of the tabular array, and the columns can be sorted past clicking the table headers.
Perform the analysis
After Samples have been assigned to groups, click the Analyze button to run the assay with default parameters.
Alternatively, you tin can edit the default assay parameters in the Options tab. For case, you can select an alternative P-value aligning method in the Options tab and click Reanalyze to run the analysis with revised parameters. Details regarding each edit choice are provided in the Edit options and features section below.
You can click the Analyze button without defining groups and retrieve UMAP, boxplot, expression density and hateful variance trend plots. These plots can be helpful in assessing normalization status and sample groupings, that is, they can aid you determine suitability of the study for further analysis and whether to utilize whatsoever adjustments to the test.
Top differentially expressed genes
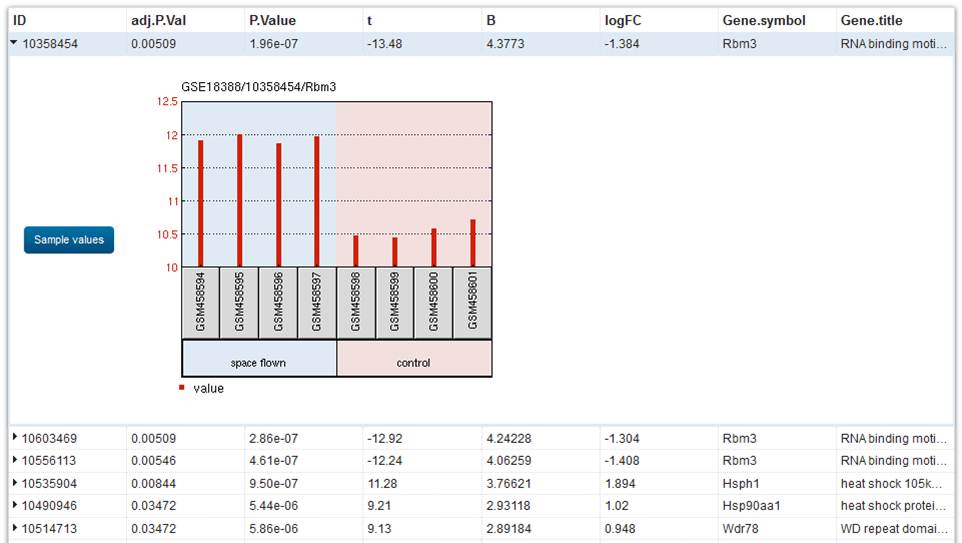
Results are presented in the browser as a tabular array of the top 250 genes ranked by P-value. Genes with the smallest P-value are the virtually pregnant. Click on a row to reveal the gene expression contour graph for that cistron. Each cherry bar in the graph represents the expression measurement extracted from the value cavalcade of the original submitter-supplied Sample tape. The Sample accession numbers and group names are listed along the bottom of the nautical chart.
Use the Select columns characteristic to change which information and annotation columns are included in the table. Information virtually the significant of the data columns is provided in the Summary statistics department.
If you want to edit the analysis parameters, you can do so in the Options tab, so click Reanalyze to use the edits.
To see more than the acme 250 genes, use the Download full table link to download the entire set of results. The downloaded file is tab-delimited and suitable for opening in a spreadsheet awarding such as Excel.
Visualization
Several graphical plots are generated to help users further explore differentially expressed genes and assess dataset quality. More item on usage of some of these plots can be found in the limma Users Guide.
| Volcano plot |  | Generated using limma (volcanoplot) A volcano plot displays statistical significance (-log10 P value) versus magnitude of alter (log2 fold change) and is useful for visualizing differentially expressed genes. Click the Explore and download link to go to the interactive plot. There, yous can mouse-over information points to see individual cistron annotation. Highlighted genes are significantly differentially expressed at a default adjusted p-value cutoff of 0.05 (reddish = upregulated, blue = downregulated). You lot can change the significance cut-off in the Options tab. A volcano plot displays the examination results for a unmarried contrast (a dissimilarity is 1 Sample grouping compared to another Sample group). Thus, if you defined more than two Sample groups in your assay, a separate plot is generated for each dissimilarity. Past default, for >ii groups of Samples, the number of contrasts presented is equal to the number of groups, and each group is compared to the adjacent in the club that they were created. Alternatively, y'all can select up to 5 custom contrasts in the Options tab. If more than ii Sample groups are defined, apply the checkboxes to toggle betwixt contrasts. Apply the Download meaning genes push to download the highlighted genes in each dissimilarity. |
|---|---|---|
| Mean difference (MD) plot | 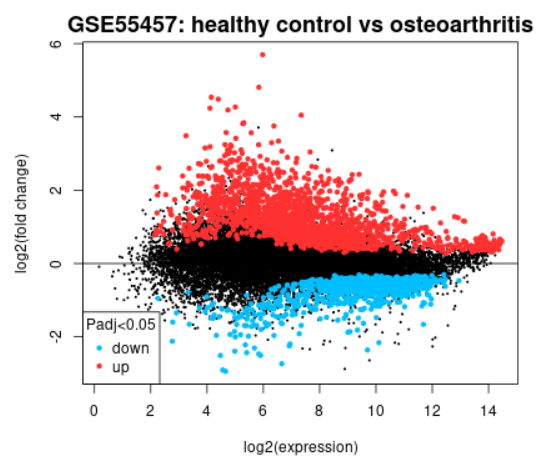 | Generated using limma (plotMD) A hateful deviation (MD) plot displays log2 fold change versus average log2 expression values and is useful for visualizing differentially expressed genes. Click the Explore and download link to become to the interactive plot. There, similar to volcano plot, you can mouse-over data points to see individual factor annotation. Highlighted genes are significantly differentially expressed at a default adapted p-value cutoff of 0.05 (crimson = upregulated, blue = downregulated). You tin change the significance cut-off in the Options tab. A mean difference plot displays the test results for a single contrast (a contrast is i Sample group compared to another Sample grouping). Thus, if yous defined more than 2 Sample groups in your assay, a separate plot is generated for each dissimilarity. By default, for >2 groups of Samples, the number of contrasts presented is equal to the number of groups, and each group is compared to the next in the guild that they were created. Alternatively, you can select up to 5 custom contrasts in the Options tab. If more than 2 Sample groups are defined, utilize the checkboxes to toggle between contrasts. Apply the Download significant genes push button to download the highlighted genes in each contrast. |
| UMAP | 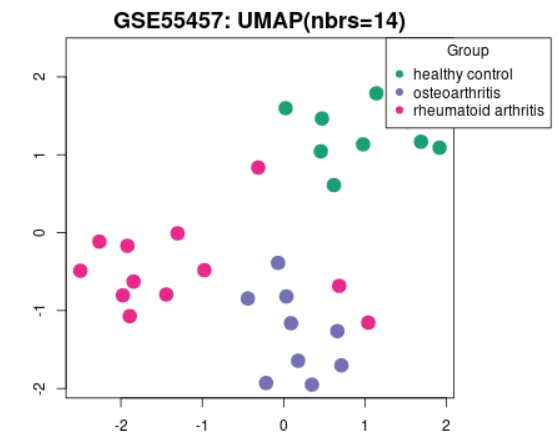 | Generated using umap Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) is a dimension reduction technique useful for visualizing how Samples are related to each other. The number of nearest neighbors used in the adding is indicated in the plot. This plot can be generated without Sample group selection, only click Analyze before defining groups. |
| Venn diagram |  | Generated using limma (vennDiagram) Use to explore and download the overlap in significant genes between multiple contrasts. The genes in each region on the Venn diagram can be downloaded by selecting the relevant contrasts. For instance, in the Venn diagram shown here, select both 'healthy control vs osteoarthritis' and 'healthy control vs rheumatoid arthritis' to download the 976 significant genes that are common to both contrasts, but non to 'osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis'. To download all significant genes for a given dissimilarity, utilize the interactive volcano or MD plot pages instead. Limitation: Data for up to v contrasts can exist plotted. When >5 groups have been defined, default beliefs is to show contrasts with the highest and lowest number of expressed genes. Alternatively, you tin can select which v contrasts to display on the Options tab. |
| Boxplot | 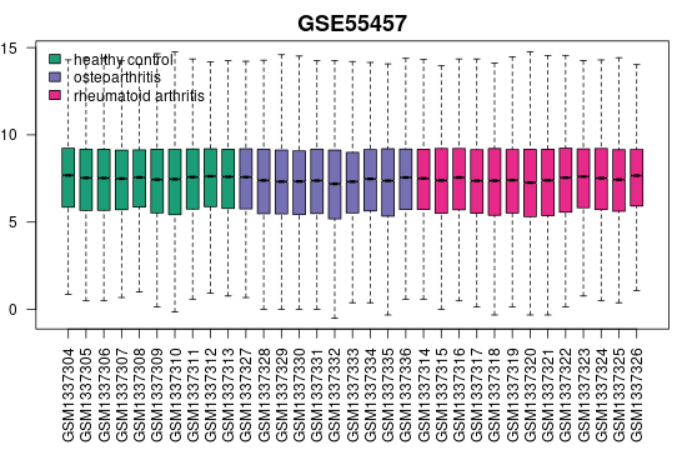 | Generated using R boxplot Use to view the distribution of the values of the selected Samples. The Samples are colored according to groups. Viewing the distribution can exist useful for determining if your selected Samples are suitable for differential expression analysis. Generally, median-centered values are indicative that the data are normalized and cross-comparable. If that is not the case, you might consider checking Force normalization in the Options tab which will utilize quantile normalization to the expression information making all selected Samples take identical value distribution. The plot shows data after log transform and normalization, if they were performed. This plot tin be generated without Sample group selection, just click Analyze before defining groups. |
| Expression density |  | Generated using R limma (plotDensities) Use to view the distribution of the values of the selected Samples. The Samples are colored according to groups. This plot complements boxplot (higher up) in checking for data normalization earlier differential expression assay. If density curves greatly differ from Sample to Sample, you might consider checking Strength normalization in the Options tab. The plot shows information after log transform and normalization if they were performed. This plot tin can be generated without Sample grouping pick, but click Analyze before defining groups. |
| Adjusted P-value histogram | 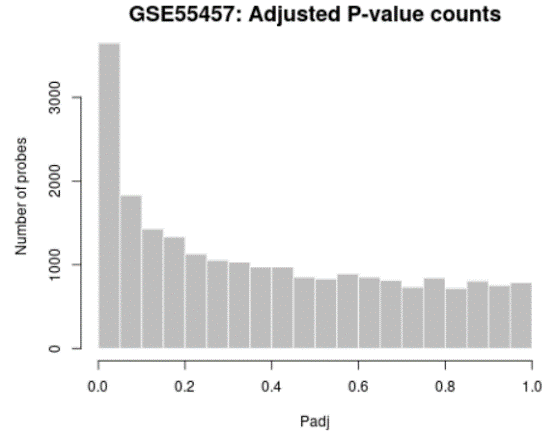 | Generated using hist Utilize to view the distribution of the P-values in the analysis results. The P-value here is the same as in the Top differentially expressed genes table and computed using all selected contrasts. While the displayed table is limited by size (250) this plot allows you to see the 'big moving-picture show' by showing the P-value distribution for all analyzed genes. |
| Moderated t-statistic quantile-quantile (q-q) plot | 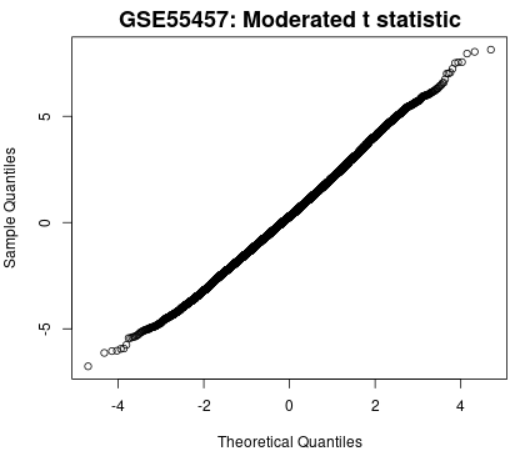 | Generated using limma (qqt) Plots the quantiles of a data sample against the theoretical quantiles of a Educatee's t distribution. This plot helps to assess the quality of the limma exam results. Ideally the points should prevarication along a straight line, meaning that the values for chastened t-statistic computed during the test follow their theoretically predicted distribution. |
| Mean-variance trend |  | Generated using R limma (plotSA, vooma) This plot is used to check the mean-variance human relationship of the expression information, after fitting a linear model. It can assist show if in that location is a lot of variation in the data. This plot can help assess whether applying the precision weights selection to take mean-variance trend into account is recommended. Precision weights improve accuracy of test results when a stiff hateful-variance tendency is nowadays. The plot does not require group choice. Each point represents a cistron. The red line is hateful-variance trend approximation that tin can be (or already is, if precision weight option in Options tab is checked) taken into account during differential cistron expression analysis. The blue line is abiding variance approximation. This plot tin can be generated without Sample group pick, simply click Analyze earlier defining groups. |
Tutorial Video
Edit options and features Back to acme
Options
Apply aligning to the P-values: Limma provides several P-value adjustment options. These adjustments, also called multiple-testing corrections, effort to correct for the occurrence of false positive results. The Benjamini & Hochberg false discovery rate method is selected by default because it is the well-nigh commonly used adjustment for microarray data and provides a proficient balance between discovery of statistically significant genes and limitation of simulated positives. If you want to change the adjustment method, go to the Options tab and select some other method. References for each method are provided below. The adjusted P-values are listed in the Adj P-value column of the results table.
Use log transformation to the information: The GEO database accepts a diverseness of data value types, including logged and unlogged data. Limma expects data values to exist in log space. To address this, GEO2R has an automobile-detect feature that checks the values of selected Samples and automatically performs a log2 transformation on values adamant not to be in log space. Alternatively, the user can select Yes to force log2 transformation, or No to override the auto-discover feature. The auto-discover feature only considers Sample values that have been assigned to a group, and applies the transformation in an all-or-none fashion.
Employ limma precision weights (vooma): The vooma office estimates the mean-variance relationship and uses this to compute advisable observational-level weights.
Force normalization: This function applies quantile normalization to the expression information making all selected samples take identical value distribution.
Category of Platform annotation to display on results: Select which category of annotation to brandish on results. Gene annotations are derived from the corresponding Platform record. Two types of annotation are possible:
NCBI generated note is available for many records. These annotations are derived past extracting stable sequence identification information from the Platform and periodically querying against the Entrez Gene database to generate consequent and up-to-date notation. Cistron symbol and Gene championship annotations are selected by default. Other categories of NCBI generated notation include Go terms and chromosomal location information.
Submitter supplied annotation is available for all records. These represent the original Platform annotations provided past the submitter. Annotation that at that place is a lot of variety in the style and content of submitter supplied annotations and they may not have been updated since the fourth dimension of submission.
Significance level cut-off: Volcano, MA and Venn plots highlight significant differentially expressed genes. The default adj-P-value significance level cut-off is 0.05. Yous tin can increase or reduce the significance level cut-off by entering a new number between 0 and 1.
Volcano, MA and Venn contrasts: Volcano and MA plots display data for a single contrast (a contrast is one Sample grouping compared to another Sample group). Thus, if you defined more than than two Sample groups in your assay, a separate plot is generated for each contrast. A maximum of five custom contrasts is presented on volcano, MA and Venn plots – for studies with >v possible contrasts, you lot can modify the contrast selection using the drop-down bill of fare.
Profile graph
This tab allows you to view a specific gene expression profile graph by entering the corresponding identifier from the ID column of the Platform record. This feature does non perform whatsoever calculations; information technology merely displays the expression values of the gene across Samples. Sample groups do not need to be defined for this feature to work.
R script
This tab prints the R script used to perform the calculation. This information can exist saved and used as a reference for how results were calculated.
Limitations and caveats Back to pinnacle
The GEO database is a public repository that athenaeum thousands of original high-throughput functional genomic studies submitted past the scientific customs. These studies represent a large diversity of experimental types and designs, and incorporate data that are processed and normalized using a broad variety of methods. GEO2R can access and analyze almost whatever GEO Series, regardless of data type and quality, so the user must exist aware of the following limitations and caveats.
Check that Sample values are comparable: GEO2R operates on Serial Matrix files which comprise data extracted straight from the VALUE column of Sample tables. Submitters are asked to supply normalized data in the VALUE column, rendering the Samples cross-comparable. The majority of GEO information do conform to this rule. GEO applies no further processing other than to perform a log2 transformation on values determined not to exist in log space (meet Options section). However, some studies, such as dual channel loop pattern data, may generate values that exercise non have a common reference and are non directly comparable. Some studies may incorporate Sample value information that are not normalized, or have a design such that the Samples were never intended to be directly compared. Yet other studies do not have sufficient replicate Samples to perform a robust statistical assay. Users should examine the original Series to empathise the experimental design, and check the 'Data processing' field or VALUE description in the original Sample records for information on what the values represent. Several plots, including boxplot and expression density can be generated without Sample group selection, just click Analyze before defining groups. These plots can help users appraise whether the distributions of values across Samples are normalized and cross-comparable.
Data type brake: GEO2R operates on data in Series Matrix files which contain data extracted directly from the VALUE column of Sample tables. Some categories of GEO Samples practice not take data tables (eastward.k., high-throughput sequencing or genome tiling arrays) and thus cannot exist analyzed using GEO2R.
Limma contrast selection: When more than 2 Sample groups are defined, GEO2R selects pairwise contrasts in a circular fashion (eg, 1 vs 2; two vs three, 3 vs iv). Thus, the elevation differentially expressed genes presented in the results table may not fully reflect the user expectation of all possible pairwise contrasts.
Within-Series brake: GEO2R operates on Serial Matrix files. Thus, analyses are restricted to Samples that occur within one Series; information technology is not possible to perform cross-Serial comparisons.
Failed jobs: Occasionally, a GEO2R analysis will fail considering some aspect of the input data is not uniform with the GEOquery or limma packages. In such cases, native BioConductor errors are reported.
10 minute timeout: GEO2R currently has a 10 infinitesimal cutoff imposed on chore processing. If the Series y'all are attempting to clarify has a big number of Samples and/or genes, the analysis may not run to completion.
More information and references Back to height
Summary statistics
GEO2R provides the following summary statistics every bit generated past the limma topTable office. More information about each statistic is provided in chapter 10 of the limma users guide.
| adj.P.Val | P-value after adjustment for multiple testing. This column is more often than not recommended equally the master statistic by which to interpret results. Genes with the smallest P-values will be the most reliable. |
|---|---|
| P.Value | Raw P-value |
| t | Moderated t-statistic (only bachelor when two groups of Samples are defined) |
| B | B-statistic or log-odds that the gene is differentially expressed (merely available when two groups of Samples are defined) |
| logFC | Log2-fold change between two experimental conditions (only available when two groups of Samples are defined) |
| F | Chastened F-statistic combines the t-statistics for all the pair-wise comparisons into an overall examination of significance for that gene (only available when more 2 groups of Samples are defined) |
General references
- Smyth, G. K. (2004). Linear models and empirical Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology, Vol. 3, No. 1, Article three.
- Smyth, Thousand. K. (2005). Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions using R and Bioconductor, R. Admirer, V. Carey, S. Dudoit, R. Irizarry, W. Huber (eds.), Springer, New York, pages 397-420.
- Sean Davis and Paul S. Meltzer (2007). GEOquery: a bridge betwixt the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 23(xiv): 1846-1847
- R documentation: Tabular array of Acme Genes from Linear Model Fit
Adjustment test references
- R documentation: Adjust P-values for Multiple Comparisons
- Benjamini, Y., and Hochberg, Y. (1995). Decision-making the false discovery charge per unit: a applied and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Gild Serial B, 57, 289-300.
- Benjamini, Y., and Yekutieli, D. (2001). The command of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Annals of Statistics 29, 1165-1188.
- Holm, S. (1979). A elementary sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scandinavian Periodical of Statistics, 6, 65-70.
- Hommel, Yard. (1988). A stagewise rejective multiple test procedure based on a modified Bonferroni test. Biometrika, 75, 383-386.
- Hochberg, Y. (1988). A sharper Bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika, 75, 800-803.
- Shaffer, J. P. (1995). Multiple hypothesis testing. Almanac Review of Psychology, 46, 561-576.
- Sarkar, Due south. (1998). Some probability inequalities for ordered MTP2 random variables: a proof of Simes conjecture. Annals of Statistics, 26, 494-504.
- Sarkar, S., and Chang, C. K. (1997). Simes' method for multiple hypothesis testing with positively dependent test statistics. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 92, 1601-1608.
- Wright, S. P. (1992). Adapted P-values for simultaneous inference. Biometrics, 48, 1005-1013.
Can Rlog Be Applied For Data With No Replicates,
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/info/geo2r.html
Posted by: johnsonimation.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can Rlog Be Applied For Data With No Replicates"
Post a Comment